The End of “De Minimis” Under Trump: A New Era for Trade and Consumers?
Introduction: A Trade Policy Earthquake
The Trump administration’s decision to suspend and eventually repeal the *de minimis* exemption for low-value imports sent shockwaves through the global trade landscape. This seemingly technical policy shift carried profound implications for businesses, consumers, and the future of international commerce. The move, framed as a protective measure for American industries, sparked intense debate about fair trade, economic competitiveness, and the evolving nature of global commerce in the digital age.
The *De Minimis* Exemption: A Trade Facilitator Under Fire
The *de minimis* exemption has long been a cornerstone of international trade, allowing goods below a certain value to enter a country without tariffs or duties. In the United States, this threshold stood at $800, enabling duty-free imports for packages valued at or below this amount. The exemption aimed to streamline customs procedures, reduce administrative burdens, and foster economic activity by facilitating the cross-border trade of small-value items.
This provision became particularly crucial with the rise of e-commerce, enabling online retailers to offer competitive prices by avoiding the complexities and costs associated with tariffs and duties. However, critics argued that the exemption had outlived its usefulness, becoming a loophole exploited by foreign companies to gain an unfair advantage over domestic businesses.
Trump’s Justification: Protecting American Interests
President Trump’s decision to target the *de minimis* exemption was driven by several key concerns. Primarily, he argued that the provision was being abused by foreign companies, particularly those in China and Hong Kong, to circumvent tariffs and duties. By shipping goods in numerous small packages, these companies could undercut American manufacturers and retailers, creating an uneven playing field.
The Trump administration also raised alarms about the potential for the *de minimis* exemption to facilitate the entry of counterfeit goods and illicit substances, including fentanyl, into the United States. The sheer volume of small packages entering the country made it difficult for customs officials to thoroughly inspect each shipment, creating opportunities for illegal activities.
Trump characterized the *de minimis* loophole as a “big scam” that needed to be addressed to protect American interests and ensure fair trade practices. His administration saw the exemption as a relic of a bygone era, ill-suited to the challenges of modern global commerce.
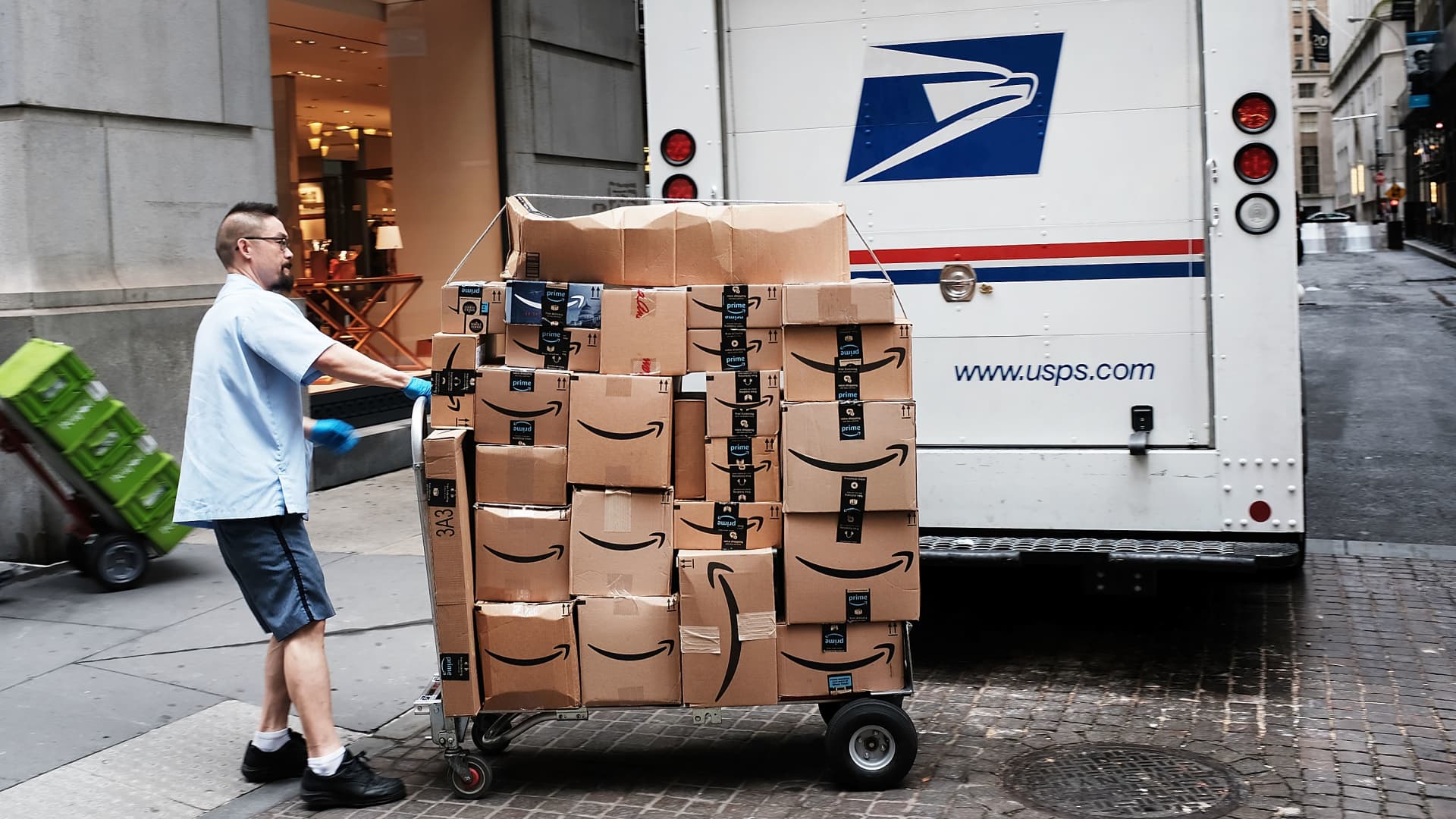
The Impact on Online Retailers: A Seismic Shift
The suspension of the *de minimis* exemption had a particularly significant impact on online retailers like Shein and Temu, which rely heavily on direct-to-consumer shipments of low-cost goods from China. These companies had capitalized on the *de minimis* provision to offer extremely competitive prices to American consumers, rapidly gaining market share in the apparel and consumer goods sectors.
By eliminating the duty-free status of these shipments, Trump’s policy increased the cost of importing goods for Shein, Temu, and similar retailers, potentially eroding their price advantage and making them less competitive in the U.S. market. This move was seen by some as a deliberate attempt to curb the growth of these Chinese e-commerce giants and protect domestic retailers from foreign competition.
The policy shift also raised questions about the future of e-commerce and the role of low-value imports in the global economy. As online shopping continues to grow, the ability to offer competitive prices hinges on minimizing import costs. The repeal of the *de minimis* exemption could force retailers to reevaluate their business models and supply chains, potentially leading to higher prices and reduced choice for consumers.
Consequences for American Consumers: A Double-Edged Sword
While the Trump administration argued that the suspension of the *de minimis* exemption would benefit American businesses, critics warned that it could lead to higher prices and reduced choice for consumers. By increasing the cost of imported goods, the policy could force retailers to raise prices, potentially impacting low-income households and those who rely on affordable products from overseas.
Additionally, the elimination of the *de minimis* exemption could reduce the availability of certain niche products that are primarily sourced from foreign countries. Consumers who value access to a wide range of goods, regardless of their origin, might find their options limited as retailers become more cautious about importing low-value items.
The policy also raised concerns about the potential for increased bureaucracy and delays in the delivery of goods. With the *de minimis* exemption in place, customs procedures were streamlined, allowing for faster and more efficient processing of small packages. The repeal of this provision could lead to longer wait times and increased administrative burdens, further impacting consumer satisfaction and retail operations.
The Broader Trade War Context: A Strategic Gambit
Trump’s decision to target the *de minimis* exemption should be viewed within the broader context of his trade war with China and his overall approach to international trade. Throughout his presidency, Trump used tariffs and other trade barriers as leverage to negotiate more favorable trade deals with other countries. The suspension of the *de minimis* exemption could be seen as another tool in this arsenal, aimed at pressuring China to address its trade practices and reduce its trade surplus with the United States.
By disrupting established trade flows and creating economic pressure, Trump hoped to force China to the negotiating table and secure concessions that would benefit American businesses and workers. Whether this strategy ultimately proved successful remains a subject of debate, but it undoubtedly had a significant impact on the global trading system.
The policy also highlighted the challenges of navigating trade relations in an increasingly interconnected world. As global supply chains become more complex and interdependent, the ability to impose unilateral trade measures becomes both more difficult and more consequential. The repeal of the *de minimis* exemption underscored the delicate balance between protecting domestic industries and maintaining the flow of goods and services across borders.
The Future of *De Minimis*: Uncertainty and Evolution
While initial reports suggested the *de minimis* exemption would end in 2027, the actual timeline and implementation remain uncertain. Policy shifts can occur quickly, particularly in the realm of international trade. The potential repeal highlights the ongoing debate surrounding the role of trade policy in shaping economic outcomes. Supporters of the repeal argue that it is necessary to protect domestic industries and ensure fair competition, while opponents contend that it will harm consumers and stifle economic growth.
The future of the *de minimis* exemption will likely depend on the evolving political landscape and the priorities of future administrations. As the global economy continues to evolve, trade policies must adapt to address the unique challenges and opportunities of the digital age. The repeal of the *de minimis* exemption serves as a reminder of the need for flexible and forward-thinking trade regulations that can balance the interests of businesses, consumers, and governments.
A Lasting Legacy: Rethinking Global Trade in the Digital Age
Regardless of the ultimate fate of the *de minimis* exemption, Trump’s actions have sparked a broader conversation about the challenges and opportunities of global trade in the digital age. The rise of e-commerce and the increasing volume of small-package shipments have transformed the landscape of international commerce, raising new questions about customs procedures, trade enforcement, and the balance between protecting domestic industries and promoting consumer welfare.
The Trump administration’s focus on the *de minimis* exemption has forced policymakers to reconsider the effectiveness of existing trade rules and regulations in addressing the unique challenges of the modern global economy. As e-commerce continues to grow and evolve, it is essential to develop trade policies that are both fair and effective, balancing the interests of businesses, consumers, and governments.
The repeal of the *de minimis* exemption also highlights the need for international cooperation in addressing the complexities of global trade. As countries grapple with the challenges of the digital economy, collaboration and coordination will be crucial in developing policies that promote economic growth, protect consumers, and ensure fair competition.
Conclusion: A Complex Legacy of Trade Disruption
President Trump’s decision to suspend and target the repeal of the *de minimis* exemption was a bold and controversial move that reflects his broader approach to trade policy. While the long-term consequences of this action remain to be seen, it has undoubtedly had a significant impact on online retailers, consumers, and the global trading system. Whether this policy ultimately proves to be beneficial for the American economy is a matter of ongoing debate, but it has certainly sparked a critical discussion about the future of trade in the digital age.
The repeal of the *de minimis* exemption serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between protecting domestic industries and fostering economic growth. As the global economy continues to evolve, trade policies must adapt to address the unique challenges and opportunities of the digital age. The legacy of Trump’s trade policies will continue to shape the future of international commerce, forcing policymakers to grapple with the complexities of a rapidly changing world.
The Echo of Disruption: Will Trade Ever Be the Same?
The end of the *de minimis* exemption under Trump marks a pivotal moment in the history of global trade. As the world navigates the complexities of the digital economy, the lessons learned from this policy shift will undoubtedly influence the future of international commerce. The echoes of disruption will continue to resonate, shaping the policies and practices that define the trade landscape for years to come.